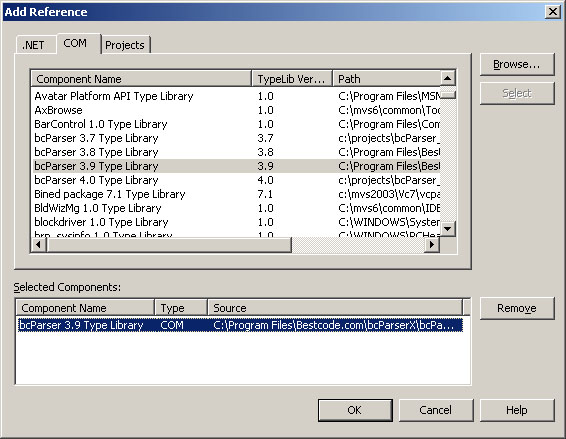
|
using System;
using BCPARSERLib;
//using System.Runtime.InteropServices;
namespace CSharpExample
{
/// <summary>
/// Summary description for Class1.
/// </summary>
class Class1
{
/// <summary>
/// The main entry point for the application.
/// </summary>
[STAThread]
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Parser p = new ParserClass(); //new parser instance.
try
{
//You can register your own event handlers to create custom functions:
p.OnExecOneParamFunc += new _IParserEvents_OnExecOneParamFuncEventHandler(onExecOneParamFunc);
p.OnExecTwoParamFunc += new _IParserEvents_OnExecTwoParamFuncEventHandler(onExecTwoParamFunc);
p.OnExec3ParamFunc += new _IParserEvents_OnExec3ParamFuncEventHandler(onExec3ParamFunc);
p.OnExecNParamFunc += new _IParserEvents_OnExecNParamFuncEventHandler(onExecNParamFunc);
//p.Expression = "x+y+z+k"; //notice that k is not valid.
//Register your own function names:
p.CreateOneParamFunc("ONE");
p.CreateTwoParamFunc("TWO");
p.Create3ParamFunc("THREE");
p.CreateNParamFunc("NP");
p.Expression = "NP(1,2,3,4)+ONE(1)+TWO(2,3)+THREE(1,2,3)+X";
//p.Expression = "AVG(7, 5)";
p.X = 5; //assign predefined var X.
p.Y = 6; //assign predefined var Y.
p.set_Variable("Z", 1); //create new var Z.
double value = p.Evaluate(); //get result.
Console.WriteLine("Answer="+value);
}
catch(Exception ex)
{
Console.WriteLine(ex.Message);
Console.WriteLine("Invalid syntax is: "+
p.GetInvalidPortionOfExpression());
}
Console.WriteLine("Press Enter to Exit.");
Console.ReadLine();
}
/// <summary>
/// Event handler to return the value of user defined functions that take one parameter.
/// Math Parser will report syntax error if exactly 1 parameter is not passed to invoke a
/// user defined function that is registered as a 1 parameter function.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="funcName">The function name whose value should be returned.</param>
/// <param name="p">The parameter value that the user defined function takes.</param>
/// <returns>Value of the user defined function funcName.</returns>
static public double onExecOneParamFunc(string funcName, double p)
{
if(funcName.Equals("ONE"))
{
return p+1; //do something with parameters.
}
throw new Exception("Unexpected function name: "+funcName);
}
/// <summary>
/// Event handler to return the value of user defined functions that take two parameter.
/// Math Parser will report syntax error if exactly 2 parameters are not passed to invoke a
/// user defined function that is registered as a 2 parameter function.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="funcName">The function name whose value should be returned.</param>
/// <param name="p1">The first parameter value that the user defined function takes.</param>
/// <param name="p2">The second parameter value that the user defined function takes.</param>
/// <returns>Value of the user defined function funcName.</returns>
static public double onExecTwoParamFunc(string funcName, double p1, double p2)
{
Console.WriteLine("FuncName: "+funcName);
if(funcName.Equals("TWO"))
{
Console.WriteLine("Returning: "+(p1+p2+2));
return p1+p2+2; //do something with parameters.
}
throw new Exception("Unexpected function name: "+funcName);
}
/// <summary>
/// Event handler to return the value of user defined functions that take three parameters.
/// Math Parser will report syntax error if exactly 3 parameters are not passed to invoke a
/// user defined function that is registered as a 3 parameter function.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="funcName">The function name whose value should be returned.</param>
/// <param name="p1">The first parameter value that the user defined function takes.</param>
/// <param name="p2">The second parameter value that the user defined function takes.</param>
/// <param name="p3">The second parameter value that the user defined function takes.</param>
/// <returns>Value of the user defined function funcName.</returns>
static public double onExec3ParamFunc(string funcName, double p1, double p2, double p3)
{
if(funcName.Equals("THREE"))
{
return p1+p2+p3+3; //do something with parameters.
}
throw new Exception("Unexpected function name: "+funcName);
}
/// <summary>
/// Event handler to return the value of user defined functions that take any numbers of parameters.
/// Enforcement of the correct number of parameters that a function supports is done within this
/// event handler. Math Parser will not accept any number of parameters and your event handler needs
/// to decide whether a particular set of parameters are ok or not.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="funcName">The function name whose value should be returned.</param>
/// <param name="values">The parameters that the user defined function takes are passed in
/// as System.Array.</param>
/// <returns>Value of the user defined function funcName.</returns>
static public double onExecNParamFunc(string funcName, ref System.Array values)
{
Console.WriteLine("FuncName is: "+funcName);
if(funcName.Equals("NP"))
{
if(values.GetLength(0)!=4)
{
throw new Exception("NP function requires 4 parameters. "+
"Number of parameters passed: "+values.GetLength(0));
}
double val = (Double)values.GetValue(0)+(Double)values.GetValue(3);
Console.WriteLine("Returning: "+val);
return val;
}
throw new Exception("Unexpected function name: "+funcName);
}
}
}
|